PartGlot: Learning Shape Part Segmentation from Language Reference Games
Juil Koo, Ian Huang, Panos Achlioptas, Leonidas Guibas, Minhyuk Sung
CVPR 2022
Abstract
We introduce PartGlot, a neural framework and associated architectures for learning semantic part segmentation of 3D shape geometry, based solely on part referential language. We exploit the fact that linguistic descriptions of a shape can provide priors on the shape’s parts – as natural language has evolved to reflect human perception of the compositional structure of objects, essential to their recognition and use. For training, we use the paired geometry / language data collected in the ShapeGlot work for their reference game, where a speaker creates an utterance to differentiate a target shape from two distractors and the listener has to find the target based on this utterance. Our network is designed to solve this target discrimination problem, carefully incorporating a Transformer-based attention module so that the output attention can precisely highlight the semantic part or parts described in the language. Furthermore, the network operates without any direct supervision on the 3D geometry itself. Surprisingly, we further demonstrate that the learned part information is generalizable to shape classes unseen during training. Our approach opens the possibility of learning 3D shape parts from language alone, without the need for large-scale part geometry annotations, thus facilitating annotation acquisition.
Juil Koo, Ian Huang, Panos Achlioptas, Leonidas Guibas, Minhyuk Sung
PartGlot: Learning Shape Part Segmentation from Language Reference Games
CVPR 2022
arXiv |
Code
Bibtex
@proceedings{PartGlot:2022,
author = {Koo, Juil and Huang, Ian and Achlioptas, Panos and Guibas, Leonidas and Sung, Minhyuk},
title = {PartGlot: Learning Shape Part Segmentation from Language Reference Games},
booktitle = {CVPR},
year = {2022}
}
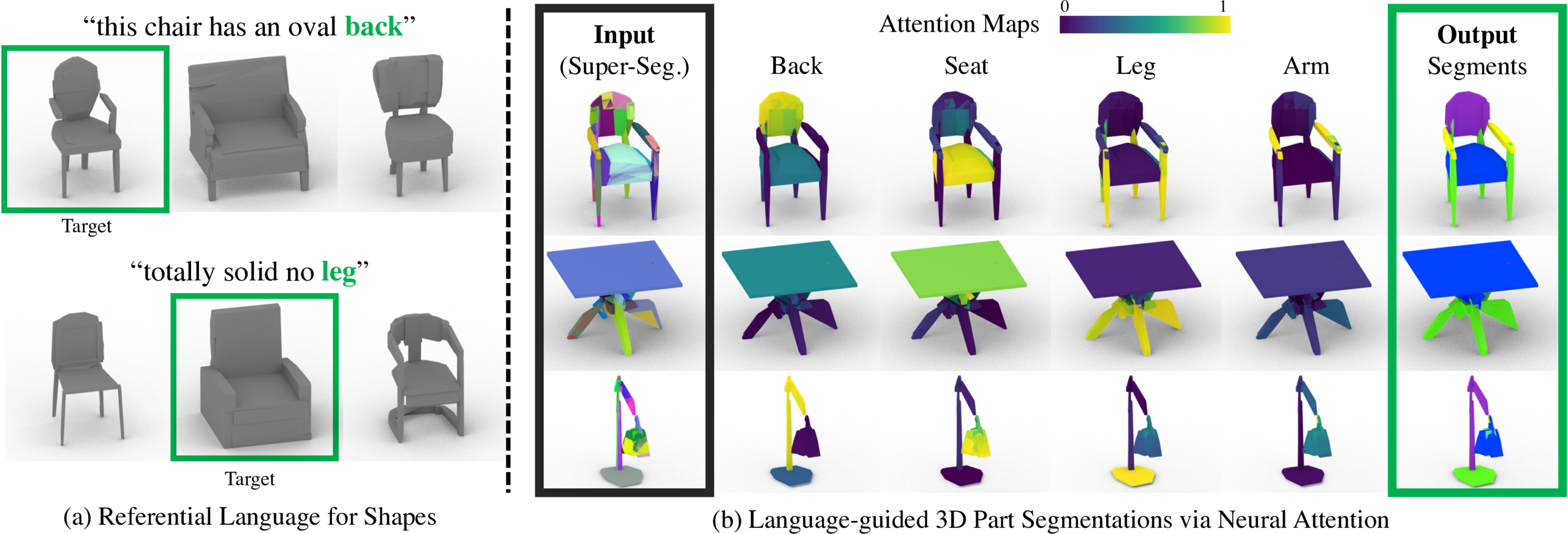
Language-guided 3D Part Segmentations via Neural Attention
The followings are random examples of our segmentation results. Refresh the webpage to see new random examples. Given unsupervised 3D super-segments of shapes (the first column) and the referential language, we learn a set of attention maps that corresponds to semantic shape parts, discovered solely by solving the language-reference problems of identifying the target shape. At test time, we obtain part segments using the attention map of a template expression: “a chair with {part name}” (the second to fifth columns). The color goes from blue to yellow for the attention weight zero to one. The final part segmentation (the sixth column) is obtained by assigning the part label with the highest attention weight to each super-segment.
See the teaser image (Figure 1) and Section A.10. in the arXiv version for more examples.
Out-of-Distribution Test
Tapping on the zero-shot learning capacity of natural language learners, and the shared part composition of common objects, we find examples of zero-shot segmentations on other categories (Airplane, Car, Lamp, and Table), extracted from learners and language concerning only chairs. Refresh the webpage to see new random examples.
See the teaser image (Figure 1) and Section A.10. in the arXiv version for more examples.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by NRF grant (2021R1F1A1045604) and NST grant (CRC 21011) funded by the Korea government(MSIT), Technology Innovation Program (20016615) funded by the Korea government(MOTIE), and grants from the Adobe and KT corporations. L. Guibas also acknowledges the support of ARL grant W911NF2120104, a Vannevar Bush faculty fellowship, and grants from the Adobe, Autodesk, and Snap corporations.